- Austin leaders consider expanding wildfire protection plan
- Large hail, strong winds and tornado threat possible into Thursday evening
- Large hail, tornado threat possible Thursday evening
- Jaccob Slavin scores in OT as the Hurricanes beat the Capitals in Game 1 of their 2nd-round series
- 5 On Your Side: What happened to cars flooded during Hurricane Helene?
Alberto, hurricane season's first named storm, makes landfall in Mexico
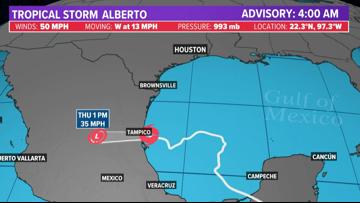
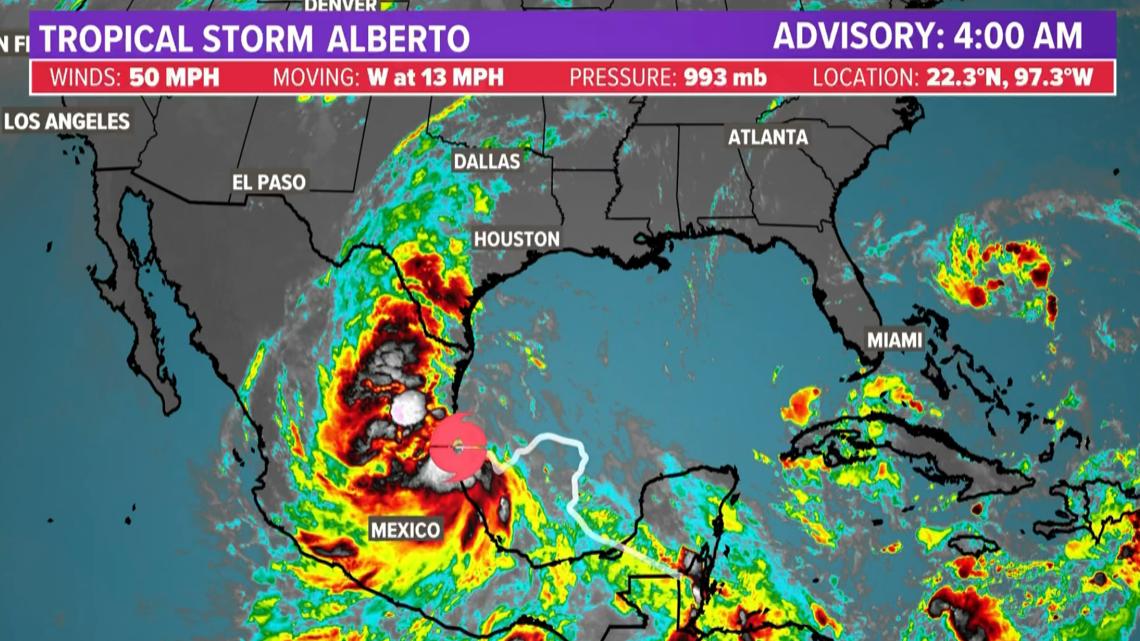
The NHC said Tropical Storm Alberto began moving inland at 6:48 a.m. Thursday near Tampico, Mexico.
HOUSTON — Tropical Storm Alberto was the first named storm of the 2024 hurricane season after forming in the Gulf of Mexico on Wednesday morning, according to the National Hurricane Center.
The NHC said Alberto made landfall around 6:48 a.m. near Tampico, Mexico on Thursday morning.
Potential Tropical Cyclone One formed into Alberto at 9:48 a.m. Wednesday.
Tropical Storm Alberto is moving west-southwest at 13 mph with maximum sustained winds of 45 mph. The storm was located near latitude 22.3 North, longitude 98.3 West.
Watches and warnings in effect
- A Tropical Storm Warning is in effect for the Texas coast from San Luis Pass southward to the mouth of the Rio Grande the northeastern coast of Mexico south of the mouth of the Rio Grande to Tecolutla. A Tropical Storm Warning means that tropical storm conditions are expected somewhere within the warning area.
Tropical Storm Alberto path


Potential threats
Rainfall
Tropical Storm Alberto is expected to produce rainfall totals of 5 to 10 inches across northeast Mexico into South Texas. Maximum totals of around 20 inches are possible across the higher terrain of the Mexican states of Coahuila, Nuevo Leon, and Tamaulipas. This rainfall will likely produce considerable flash and urban flooding along with new and renewed river flooding. Mudslides are also possible in areas of higher terrain across northeast Mexico.
Storm surge
The combination of a dangerous storm surge and the tide will cause normally dry areas near the coast to be flooded by rising waters moving inland from the shoreline. The water could reach the following heights above ground somewhere in the indicated areas if the peak surge occurs at the time of high tide:
- Sargent, TX to Sabine Pass, TX…2-4 ft
- Galveston Bay…2-4 ft
- Mouth of the Rio Grande, TX to Sargent, TX…1-3 ft
- Sabine Pass, TX to Vermilion/Cameron Parish Line, LA…1-3 ft
The deepest water will occur along the immediate coast near and to the north of the landfall location, where the surge will be accompanied by large and dangerous waves. Surge-related flooding depends on the relative timing of the surge and the tidal cycle and can vary greatly over short distances.
Storm surge will raise water levels by as much as 1 to 3 feet above normal tide levels along the immediate coast of northeastern Mexico in areas of onshore winds north of where the center makes landfall. Near the coast, the surge will be accompanied by large and destructive waves.
Wind
Tropical storm conditions are expected within the warning area today through early Thursday.
Tornadoes
A couple of tornadoes are possible today and tonight across parts of Deep South Texas and Southeast Texas.
Surf
Swells generated by Alberto will affect the coast of Texas and northeastern Mexico through Friday. These swells are likely to cause life-threatening surf and rip current conditions.
Track the storm
Hurricane season 2024 forecast
Earlier this month, Colorado State University released its forecast update for the 2024 hurricane season, maintaining that it will be a busy one. In April, they predicted that we could see 23 named storms and 11 hurricanes with five becoming major hurricanes. They blame the extremely warm tropical Atlantic and likely “La Niña” as the primary reasons.
RELATED: Colorado State University releases hurricane season forecast update, maintains it will be a busy one
On average, the Atlantic sees about 14 named storms each hurricane season. Of those, seven become hurricanes with three becoming major (Category 3 or above) storms.
Why such an active season? Dr. Phil Klotzbach, lead forecaster at CSU, says it’s because of two main factors — above-normal sea surface temperatures and expected La Niña conditions this summer. The warm water adds more energy to the tropics, making fuel for these storms more available. But perhaps more importantly, La Niña usually reduces vertical wind shear.
Winds blowing across a developing or mature tropical system can keep a budding system from developing and weaken stronger storms. This reduces the total storm count. But when La Niña conditions are in place, this wind shear is often reduced. That, combined with the warm ocean surface temps is why Dr. Klotzbach believes more storms than normal will form.