- Report: Coastal flooding could threaten 1.4 million homes by midcentury
- Caught on camera | Tornado touches down in Missouri
- Carolina Hurricanes playoff tickets go on sale next week
- Storms kill 6 in the South and Midwest as forecasters warn of catastrophic rains, floods this week
- Weather Impact Alert: Cold front could trigger severe weather in Houston area this weekend | See timeline
Hurricane Beryl regains Cat. 4 strength as it moves over Carriacou Island
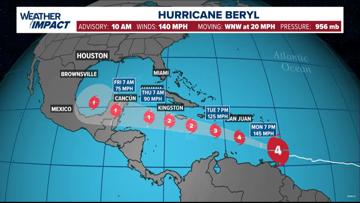
At 10 a.m., Beryl had maximum sustained winds at 140 miles per hour. It’s moving to the west-northwest at 20 mph.
HOUSTON — Hurricane Beryl bore down on the southeast Caribbean early Monday, regaining Category 4 strength after briefly dropping to Category 3.
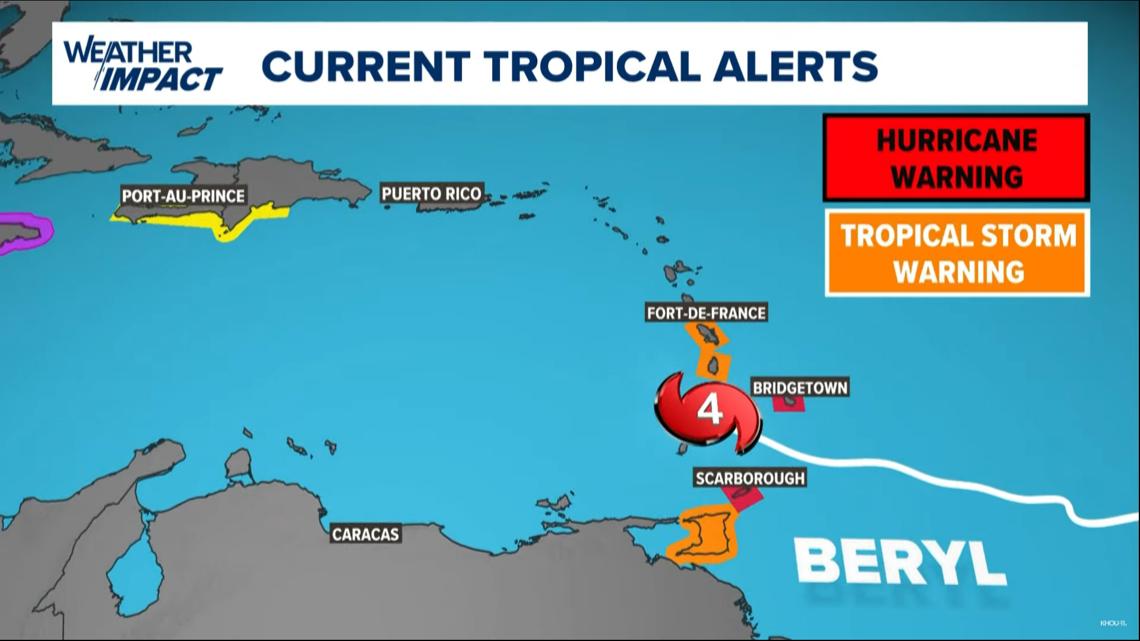
Hurricane warnings were in effect for Barbados, Grenada, St. Lucia, Tobago and St. Vincent and the Grenadines as thousands of people hunkered down in homes and shelters hoping for the best.
“It’s going to be terrible,” Ralph Gonsalves, prime minister of St. Vincent and the Grenadines, said ahead of the storm as he urged people to stay indoors “and wait this monster out.”
CURRENT LOCATION/PATH: With an update at 10 a.m. Monday, Beryl was a Category 4 storm with maximum sustained winds of 140 mph, moving west-northwest at 20 mph. (Update in Spanish).
The last strong hurricane to hit the southeast Caribbean was Hurricane Ivan nearly 20 years ago, which killed dozens of people in Grenada.
Beryl forecast cone

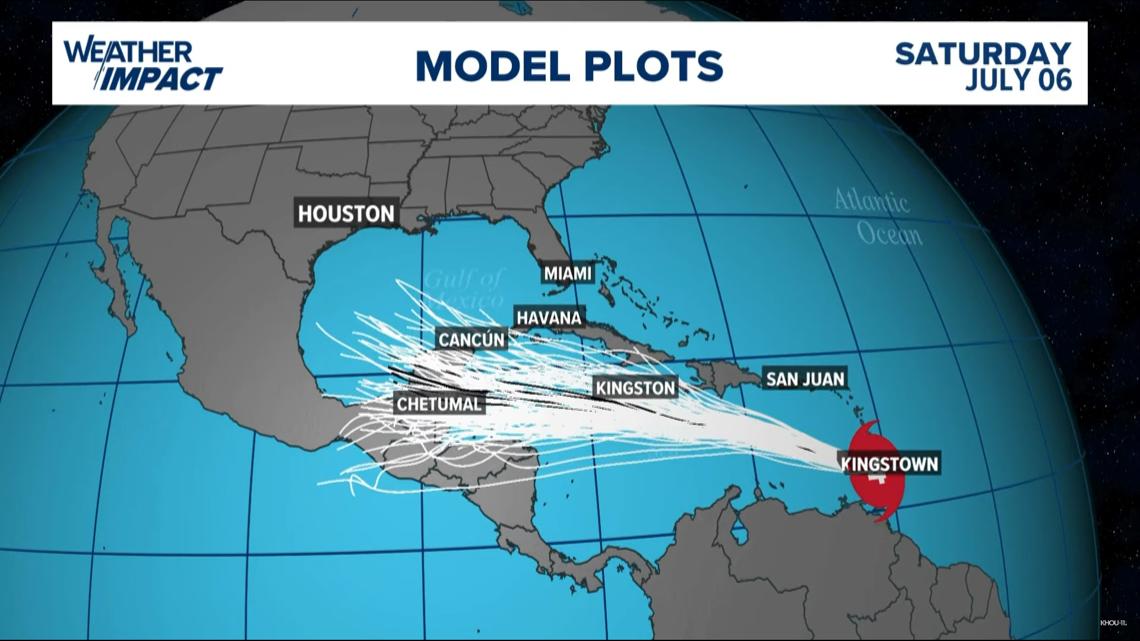
Beryl spaghetti models

Beryl was located 35 miles (55 kilometers) east-southeast of Grenada late Monday morning. It had maximum sustained winds of 140 miles west-northwest at 20 mph (31 kph). It was a compact storm, with hurricane-force winds extending 40 miles (65 kilometers) from its center.
A tropical storm warning was in effect for Martinique and Trinidad. A tropical storm watch was issued for Dominica, Haiti’s entire southern coast, and from Punta Palenque in the Dominican Republic west to the border with Haiti.
Forecasters warned of a life-threatening storm surge of up to 9 feet (3 meters) in areas where Beryl will make landfall, with 3 to 6 inches (7.6 to 15 centimeters) of rain for Barbados and nearby islands and possibly 10 inches in some areas (25 centimeters), especially in Grenada and the Grenadines.
“This is a very dangerous situation,” warned the National Hurricane Center in Miami.
The storm was expected to weaken slightly over the Caribbean Sea on a path that would take it just south of Jamaica and later toward Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula as a Category 1.
“It should be emphasized that Beryl is forecast to remain a significant hurricane during its entire trek across the Caribbean region,” the National Hurricane Center said.
Officials in some southeast Caribbean islands announced controlled shutdowns of electricity and warned of water outages ahead of the storm, urging people to seek shelter. They warned of landslides and flash flooding as they shuttered schools, airports and government offices.
Hours before the storm, Barbadian Michael Beckles said he feared the worst for his island despite witnessing how people were taking it seriously.
“As prepared as we can try to be, there are a lot of things that we can’t control,” he said. “Electricity probably will go. We’ll have issues with water. There are a lot of houses that are not ready for a storm like this.”
Watches and warnings in effect
Hurricane warnings were in effect for Barbados, Grenada, St. Lucia, Tobago and St. Vincent and the Grenadines.A tropical storm warning was in effect for Martinique and Trinidad. A tropical storm watch was issued for Dominica, Haiti’s entire southern coast, and from Punta Palenque in the Dominican Republic west to the border with Haiti.

Track the storm
Hurricane Season links
Hurricane season 2024 forecast
Colorado State University released its forecast update for the 2024 hurricane season, maintaining that it will be a busy one. In April, they predicted that we could see 23 named storms and 11 hurricanes with five becoming major hurricanes. They blame the extremely warm tropical Atlantic and likely “La Niña” as the primary reasons.
RELATED: Colorado State University releases hurricane season forecast update, maintains it will be a busy one
On average, the Atlantic sees about 14 named storms each hurricane season. Of those, seven become hurricanes with three becoming major (Category 3 or above) storms.
Why such an active season? Dr. Phil Klotzbach, lead forecaster at CSU, says it’s because of two main factors — above-normal sea surface temperatures and expected La Niña conditions this summer. The warm water adds more energy to the tropics, making fuel for these storms more available. But perhaps more importantly, La Niña usually reduces vertical wind shear.
Winds blowing across a developing or mature tropical system can keep a budding system from developing and weaken stronger storms. This reduces the total storm count. But when La Niña conditions are in place, this wind shear is often reduced. That, combined with the warm ocean surface temps is why Dr. Klotzbach believes more storms than normal will form.